UNECE
Context
The Technical Committee (TC) is the backbone of OICA. This Committee has the duty to address technical issues which affect Automobile Manufacturers within an International context, especially those which call for external representation, and to communicate OICA’s position on these issues to other parties, as appropriate.
The primary task of the TC is to represent the interests of the Automobile Manufacturers, among others, within the framework of UNECE World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations (WP.29) and its subsidiary committees and working groups, directly, or indirectly by overseeing the activities of subsidiary OICA Groups of Experts
The progressive globalization of the automobile manufacturing and marketing increased the benefits of harmonization for the public authorities, for the automobile manufacturers and of course for the vehicle users. This is why the TC gradually focused its skills on the harmonization of technical standards.
WP.29 is a unique worldwide forum of negotiations, between all countries in the world, to establish and maintain international motor vehicle regulations. It is active within the institutional framework of the UNECE Inland Transport Committee (ITC).
Activities
OICA is at the centre of the negotiations taking place at WP.29 since the automobile manufacturers produce the goods under discussions.
The TC organizes the representation of the manufacturers in these negotiations so as the governments are educated on the limits and potentials of the existing and new technologies to best conduct their domestic and international policies in terms of vehicle safety, emissions, antitheft, connectivity, automation, fuel consumption. OICA’s role is also to support the introduction of innovative vehicle technologies.


Organization
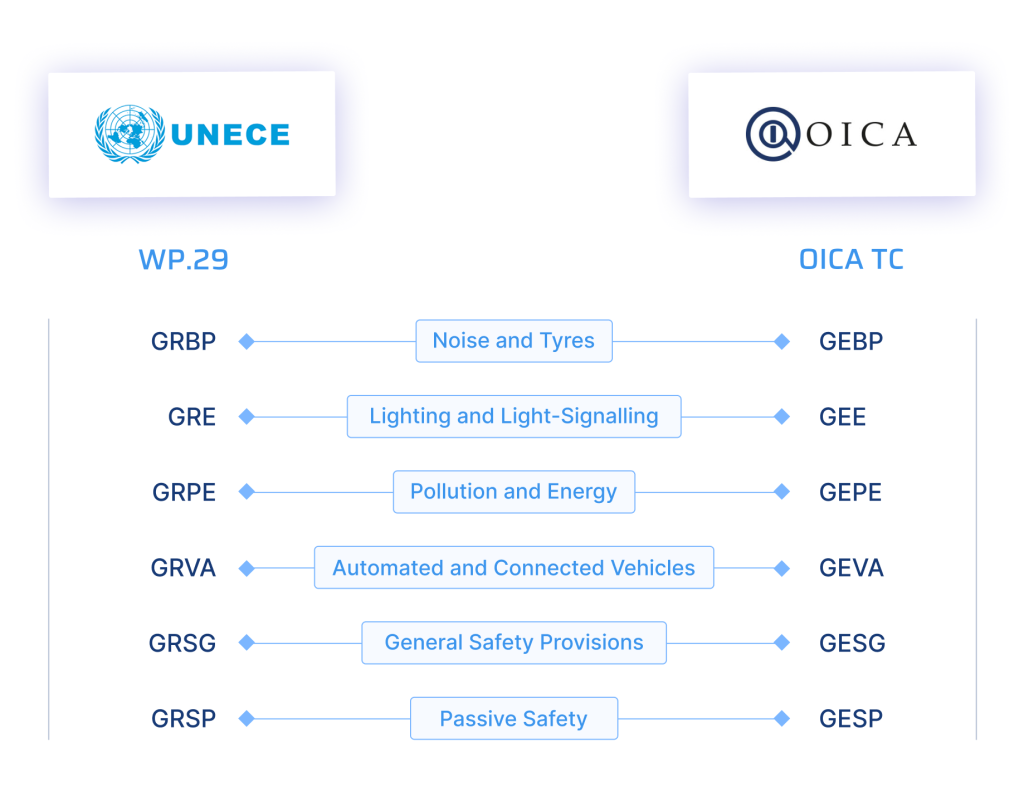
The TC’s structure mirrors that of the WP.29 to streamline the manufacturer’s impact at the Forum. WP.29 established six permanent Working Parties (GRs), i.e. subsidiary bodies that consider specialized tasks, consisting of professionals with a specific expertise, collectively responsible for governing the entire architecture and features of passenger cars, light trucks, heavy trucks, busses and coaches.
The OICA TC mirrors this as aside.
WP.29 usually meets three times a year in sessions of about three days.
Each of the WP.29 Working Parties (GRs) holds two sessions per year, while meetings of the informal working groups are scheduled according to rules that are set up in each of them, depending on their specific needs. Each of these sessions are prepared by the mirroring OICA body (GEs).
WP.29 Links :
GEBP is the OICA TC subsidiary body mirroring GRBP, the Working Party on Noise and Tyres (Groupe Rapporteur Bruit et Pneumatiques – GRBP), a subsidiary body of WP.29, that prepares regulatory proposals on vehicle noise and tyres.
GEBP systematically prepares the sessions of GRBP some weeks in advance to ensure the proper representation of the manufacturers’ interests in the debates covering the regulatory proposals. GEBP is organized so as the interests of the heavy commercial vehicle (HCV) manufacturers are covered as well as those of the light duty vehicle manufacturers.
GEE is the OICA TC subsidiary body mirroring GRE, the Working Party on Lighting and Light-Signalling (Groupe Rapporteur Eclairage – GRE), a subsidiary body of WP.29 that prepares regulatory proposals on active safety focusing on vehicle Lighting and Light-Signalling.
GEE prepares the forthcoming sessions of GRE about one month in advance so as all regulatory proposals under discussion at GRE are scrutinized and addressed. OICA have an active role at GRE for promoting the evolution of the lighting technology in the regulatory proposals. GEE and GRE make the distinction between the light emitting devices that ensure the vehicle to be seen from the road illumination devices that assist the driver in seeing the road in low illumination conditions (nighttime).
GEPE is the OICA TC subsidiary body mirroring GRPE, the Working Party on Pollution and Energy (Groupe Rapporteurs Pollution-Energie – GRPE), a subsidiary body of WP.29 that prepares regulatory proposals on pollution and energy efficiency.
The OICA members attend the GEPE preparatory sessions anticipating the GRPE mirrored subsequent sessions in view of being as pro-active as possible in the latter. GEPE works in close collaboration with the OICA’s associated member ACEA (European Manufacturers’ Association) since the European Commission shares their strong views and policies at GRPE.
GEVA is the OICA TC subsidiary body mirroring GRVA, the Working Party preparing draft regulations, guidance documents and interpretation documents for adoption by the parent body, WP.29. GRVA deals with safety provisions related to the dynamics of vehicles (braking, steering, stability), Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), Automated Driving Systems (ADS) and well as Cyber Security (CS) provisions.
By attending the GEVA meetings, the OICA members get prepared to the GRVA sessions that usually take place three times a year in sessions of about 4 days. GEVA works in close cooperation with the association of suppliers (CLEPA) since the provisions on dynamic and active safety systems are similarly affecting the active safety systems (produced by the suppliers) and the vehicles themselves (produced by the manufacturers).
GESG is the OICA TC subsidiary body mirroring GRSG, the Working Party subsidiary body of WP.29, that prepares regulatory proposals on general safety to in particular for buses and coaches.
GESG covers a wide panel of subjects going from the resistance to fire of interior fittings to safety performance of the vehicle glazing, through anti-theft systems and structural resistance of public transport vehicles. GESG is the OICA body that prepares the GRSG sessions organized by the UNECE WP.29.
GESP is the OICA TC subsidiary body mirroring GRSP, the Working Party on Passive Safety subsidiary body of the WP.29 that prepares regulatory proposals on passive safety. This group of experts conducts research and analysis to develop passive safety requirements for vehicles. Passive safety addresses all measures protecting the vehicle user at the time of an event (safety belts, deformable chassis, headrests, etc.), but also electric battery safety and hydrogen vehicle safety.
Experts attending the GESP meetings are skilled in all that matters with protection systems including child restraint systems, pedestrian protection, occupant protection, children left in vehicles, etc. they prepare the manufacturer’s behaviour and positions in view of the GRSP sessions that take place twice a year.